
This is simply due to the fact that zinc is more reactive than gold and thus it will react faster with air.
#METAL ION REACTIVITY SERIES SERIES#
For example, the Reactivity Series will show you immediately why coins made of zinc metal look dull after some time while silver and gold coins remain bright and shiny for long period of time. This is useful because it allows you to predict how a particular metal will undergo a certain chemical reaction. Metals are listed in the Reactivity Series from the most reactive to the least reactive. Today, we shall take a look at The Reactivity Series of Metals.
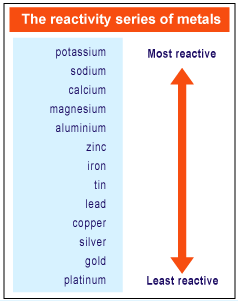
Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd 2005.In the previous blog post, we have discussed on the physical properties of pure metals as well as the four main reasons why we use metals in the form of alloys. Longman Pocket Study Guide 'O' Level Science-Chemistry by Lim Eng Wah Chapter 8 pg 190.

Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd 2005. Science in Focus, Chemistry for GCE 'O' Level by J G R Briggs Chapter 11 pg 172.Only a metal higher in the reactivity series will displace another. Therefore the elemental metal will 'displace' the ionic metal over time, thus the two swap places. When a metal in elemental form is placed in a solution of a metal salt it may be, overall, more energetically feasible for this "elemental metal" to exist as an ion and the "ionic metal" to exist as the element. However it is defined by the nature of the metals in single displacement reactions. The reactivity series determines qualitatively characteristics such as the reactions with water, air and acids as demonstrated above. does not readily give up electrons in reactions to form positive ions.does not react vigorously and quickly with chemicals.readily gives up electrons in reactions to form positive ionsĪ metal 'low down' in the reactivity series:.reacts vigorously and quickly with chemicals.Higher education and standard level are required to study more metals as shown above.Ī metal 'high up' in the reactivity series: The simplified version that is taught in the GCSE and GCE 'O' Level chemistry course, as the basic, are listed below. See Table of standard electrode potentials). The reactivity series has applications in electrochemistry, where two dissimilar metals are chosen as electrodes of a battery (though the above table is not exact for this purpose. Metals that can replace hydrogen within acids but not water are listed in the middle of the activity series, for example zinc replaces hydrogen in sulfuric acid:

For example, sodium is highly active and thus able to replace hydrogen from water:Ģ Na (s) + 2 H 2O (l) → 2 NaOH (aq) + H 2 (g) Here is a series of some of the most common metals, listed in descending order of reactivity.Ī metal can replace metals listed below it in the activity series, but not above. This is markedly different from the table below. The reactivity series taught in the US is defined by the ease of oxidation and corresponds to the ordering of the table of standard electrode potentials. In the UK a reduced version of the series below is taught as part of the GCSE chemistry course, leading to various mnemonics being invented to aid memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
